BANK OF GREECE
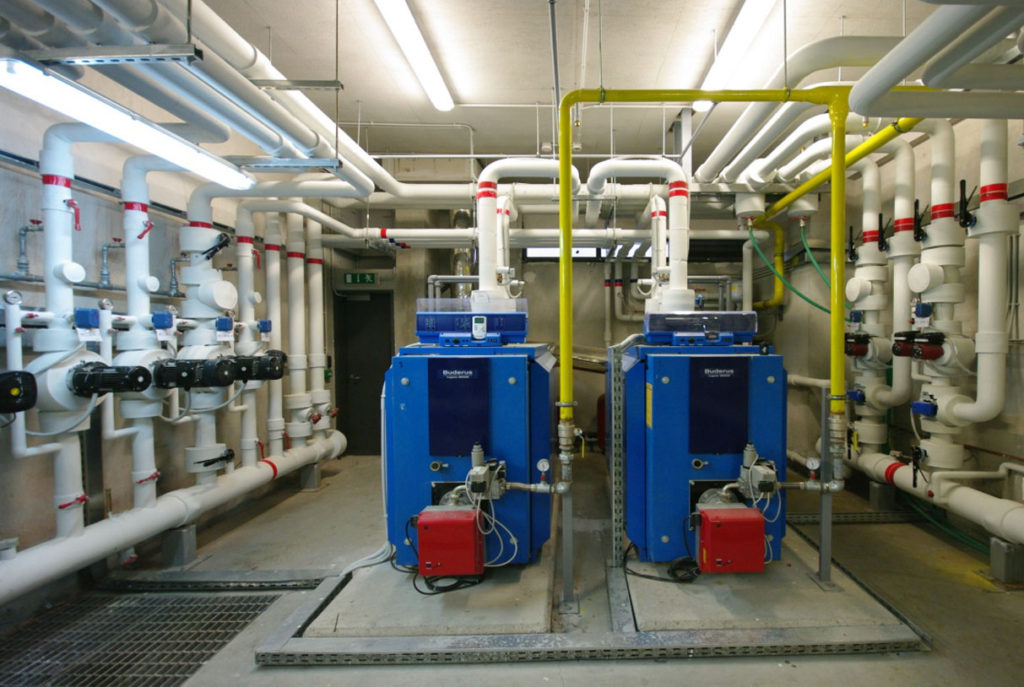
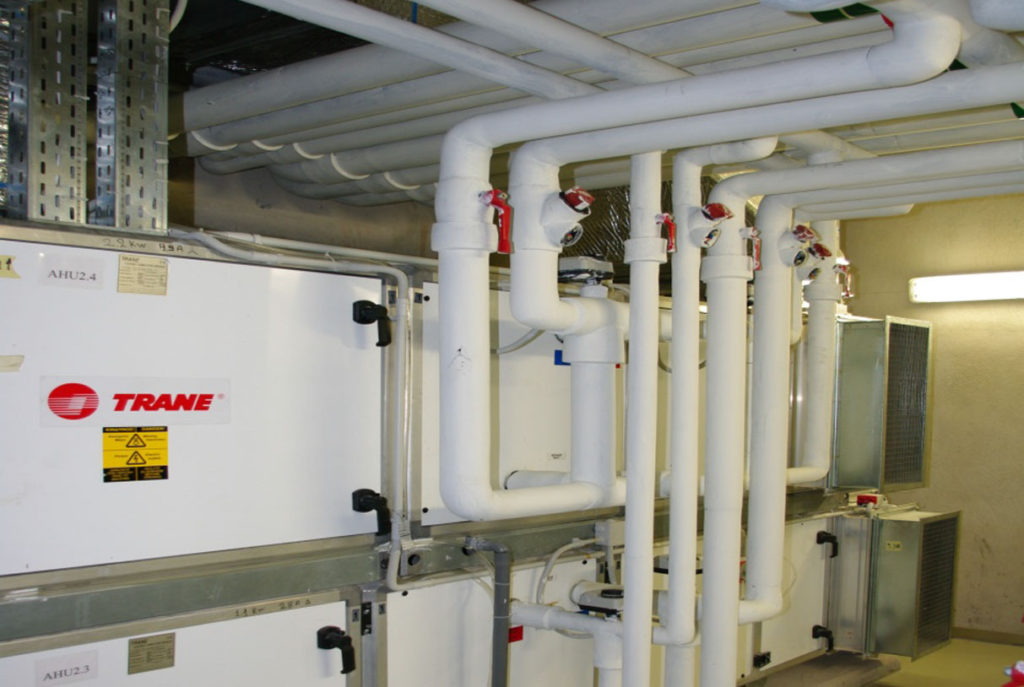
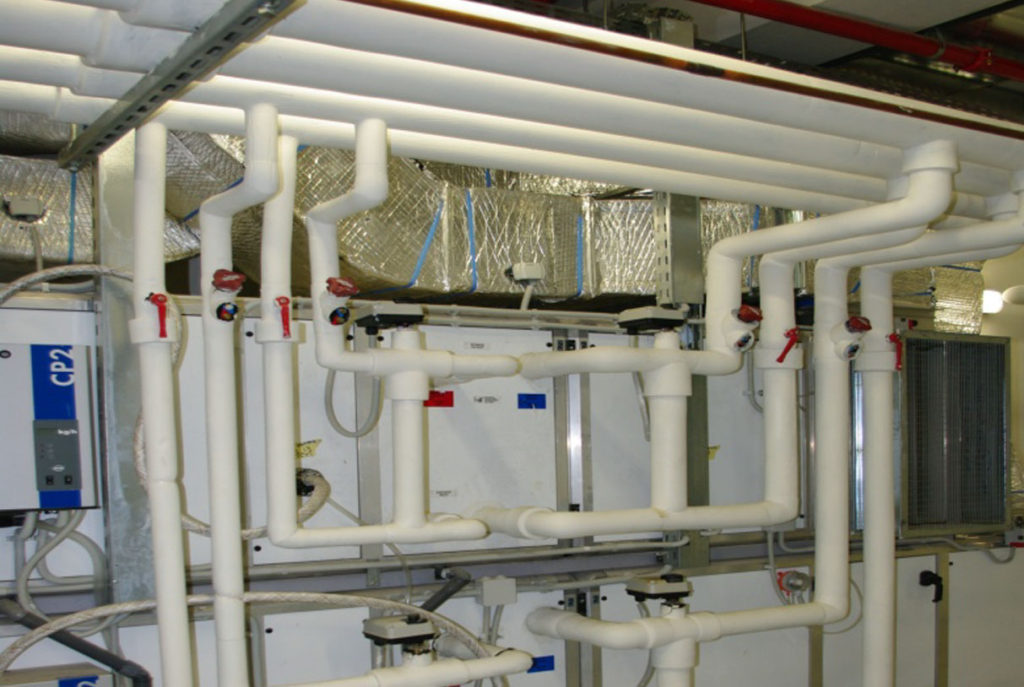
Firefighting Collector, Boiler House, Air Conditioning Network, Air Conditioning Network
The Bank of Greece is the Central Bank of the country. It was founded in 1927 on the basis of an Annex to the Geneva Protocol and began operating in May 1928. It has been set up in the form of a public limited company. Athens is defined by its Articles of Association, while it maintains 17 Branches, 32 Agencies and 3 Gates throughout Greece and the National Central Banks of the Member States of the European Union (EU) belonging to the euro area. Since then, the Bank of Greece has been contributing to the achievement of the objectives and the fulfillment of the tasks of the Eurosystem, which is charting and implementing monetary policy in the euro area. nnThe Bank of Greece is responsible for the implementation of the monetary policy of the Eurosystem in Greece and the preservation of the stability of the Greek financial system. The primary purpose of its Articles of Association is to ensure the stability of the general price level. To the extent that the achievement of its primary purpose is not affected, the Bank supports the general economic policy of the government. In the exercise of its responsibilities, its institutional, personal and functional independence has been ensured, as well as the exercise of democratic control by the Parliament.nn
INFORMATION
- Region THESSALONIKI
- Description MONEY VOLT
- Type of Project Firefighting
- Air conditioning
- Water supply
- Drains



 en
en  el
el




